Date: Sat, Oct 8, 2011 at 3:53 AM
Subject: ))))Vu & Company(((( ***Web Designing walooonn***
To: vu-and-company <vu-and-company@googlegroups.com>, dare-arqam-vu@googlegroups.com
Strings | ||||
| A string is commonly considered to be a sequence of characters stored in memory and accessible as a unit.Strings in java are represented as objects.
String Concatenation
"+" operator is used to concatenate strings – System.out.pritln("Hello" + "World") will print Hello World on console
String concatenated with any other data type such as int will also convert that datatype toString and the result will be a concatenated String displayed on console. For example,
– int i = 4; – int j = 5;
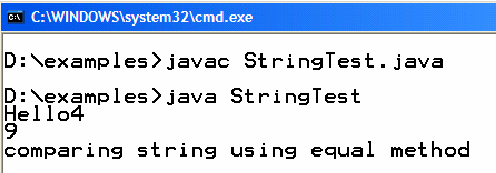
System.out.println ("Hello" + i) will print Hello 4 on screen
– However System,.out..println( i+j) ; will print 9 on the console because both i and j are of type int.
Comparing Strings
For comparing Strings never use == operator, use equals method of String class.
– == operator compares addresses (shallow comparison) while equals compares values (deepcomparison) E.g string1.equals(string2)
Example Code: String concatenation and comparison
public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 4; int j = 5;
System.out.println("Hello" + i); // will print Hello4
String s1 = new String ("pakistan"); String s2 = "pakistan";
if (s1 == s2) { System.out.println("comparing string using == operator");
}
if (s1.equals( s2) ) { System.out.println("comparing string using equal method"); } } }
On execution of the above program, following output will produce
| ||||
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.